Do You Ovulate On Birth Control?
If you have recently started taking birth control pills, or have been taking them for a while, you may wonder how it affects your body, or namely, ovulation.
Regardless of the reason you are here, you can read this article to find out how birth control affects ovulation and more.
In this article:
- What is Ovulation?
- What is Birth Control?
- How Does Birth Control Work?
- Birth Control and Ovulation
- How to Stop Using Birth Control
What is Ovulation?
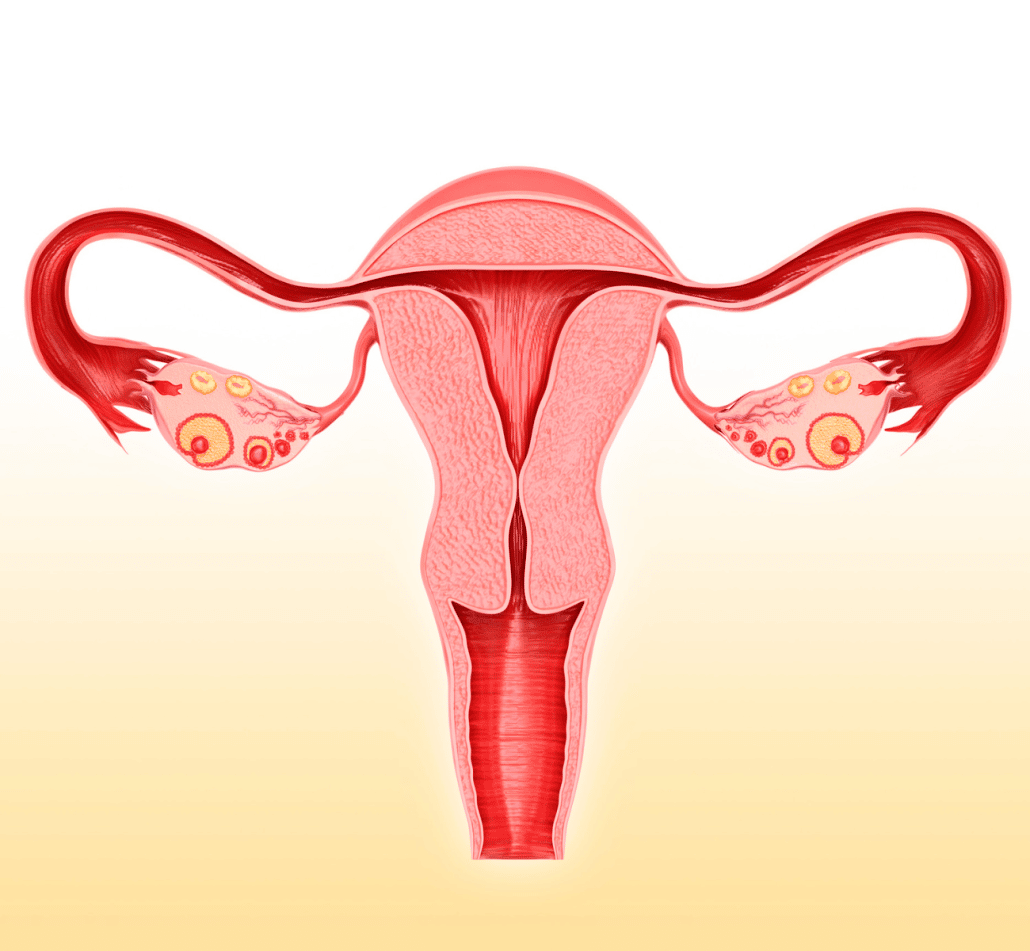
First, to understand how birth control pills work, we first need to know how the menstrual cycle works!
Each month, your body goes through the menstrual cycle.
The menstrual cycle is what helps your body to prepare for pregnancy, and it usually lasts for 28 days, although the length can vary from anywhere between 21 and 40 days in length.
The first day of your menstrual cycle is when menstruation, or your menstrual period, begins.
At around the middle of your menstrual cycle (typically day 14, but this can vary from day 10 to day 16), ovulation begins.
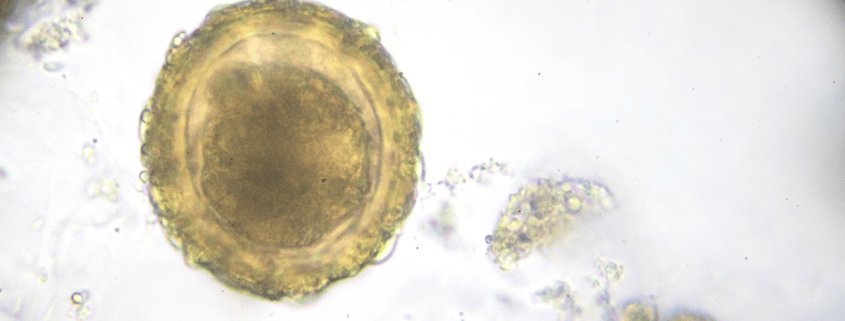
Ovulation is the phase of your menstrual cycle in which a mature egg is released from the ovaries- triggered by a sudden increase in estrogen.
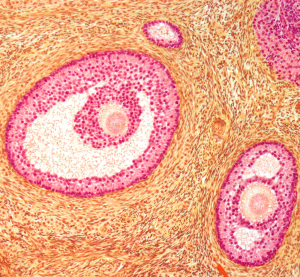
During the ovulation phase, fluid-filled spaces, called follicles, develop.
The most mature follicle (called the dominant follicle) containing a mature egg ruptures following an LH surge (12 to 24 hours prior), releasing the egg.
The remaining follicles then wither away.
The mature egg- or ovum- travels down into the fallopian tubes, towards the uterus, where it awaits fertilisation- following unprotected sexual intercourse.
If the egg is not fertilised, it is reabsorbed into the uterine lining and menstruation begins again.
If it egg is fertilised, then the fertilized egg travels to the uterine lining, where implantation occurs.
How to Know When You Are Ovulating
There are several ways which can be used to determine whether or not you are ovulating.
Firstly, you can use ovulation test kits.
Ovulation test kits work by detecting LH surges (sudden spikes in the luteinising hormone levels). A positive ovulation test result indicates that you are experiencing an LH surge, which often precedes ovulation by between 12 and 24 hours.
You can read more about LH surges and ovulation here.
Paying attention to your ovulation symptoms can also help you to identify when you may be ovulating.
Below are some potential ovulation symptoms:
- Pelvic or lower abdominal cramping (ovulation pain)
- Brown discharge or light spotting
- Cervical changes (high position and softer)
- Breast tenderness
- Sore nipples
- Bloating
- Heightened sense of smell
- Diarrhoea
- Changes in libido
- Nausea
- Weight gain
- Headaches
What is Birth Control?
Birth control- otherwise known as contraception- is any device, method or medicine which is used to prevent pregnancy.
There are several different kinds of birth control methods, including hormonal birth control pills, birth control shots, contraceptive implant and more.
How Does Birth Control Work?
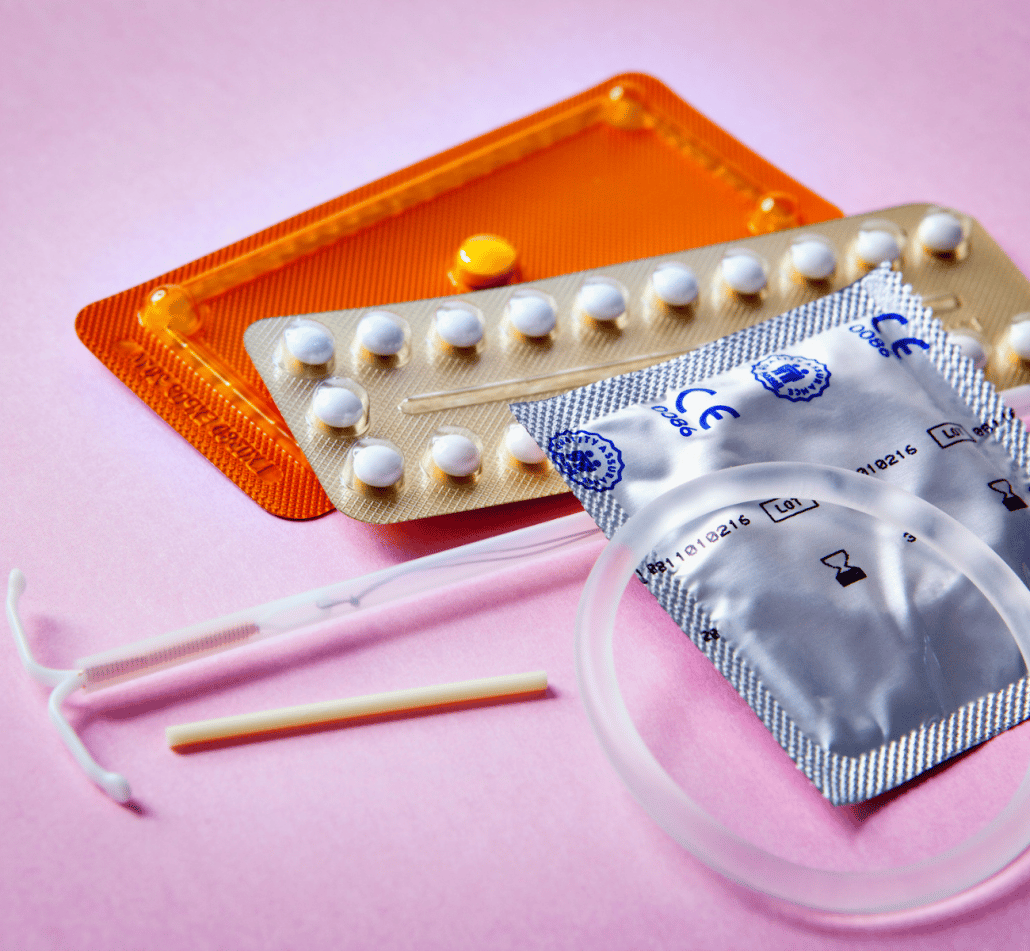
Birth control works by either preventing or suppressing ovulation through hormones.
There are many different forms of birth control methods, or contraception.
Below is each form of birth control and how they work:
- Birth Control Pill – Birth control pills fall into two categories. These categories are combination pills– which include both progesterone and estrogen with one pill required to be taken at the same time each day- and progestin-only pills, which contain only progesterone and must be taken within the same 3-hour window daily, in order to be effective. If you are taking the progestin-only pill (otherwise known as the mini pill), you should note that there is some suppression of ovulation, but there is still a chance that ovulation will occur.
- Birth Control Shot (Depo Provera) – The birth control shot is a birth control method taken by injection, every 3 months. It contains the hormone progestin, which helps to prevent ovulation.
- Birth Control Patch – The birth control patch contains the same hormones as the combination birth control pill- estrogen and progesterone- which is released into the bloodstream to prevent ovulation.
- Contraceptive Implant (Nexplanon) – The contraceptive implant is a tiny, flexible plastic rod which is placed under the skin of your upper arm by a doctor or nurse. The contraceptive implant releases a hormone, called progestogen, into your bloodstream to prevent pregnancy. The contraceptive implant lasts for 3 years before it needs to be replaced.
- Vaginal Ring (NuvaRing) – The vaginal ring is a small, soft and plastic ring that you place inside of your vagina. The NuvaRing releases a constant dose of the progesterone and oestrogen hormones into the blood stream, in order to prevent pregnacy.
- Hormonal Intrauterine Device (IUD)– The Hormonal Intrauterine Device (IUD) are…. Hormonal IUDs work by making your cervical mucus thicker, making it harder for sperm to reach the egg. They also release the hormone progestin, in order to prevent ovulation.
Birth Control and Ovulation
Do you Ovulate Whilst on Birth Control?
So, do you ovulate on birth on birth control?
If you are taking the following forms of hormonal birth control, then ovulation will be prevented each cycle:
- Combination Birth Control Pills
- Vaginal Ring (NuvaRing)
- Birth Control Patch
There is a chance that progestin-only forms of birth control may not be consistent in preventing ovulation. The hormonal birth control options that are likely to prevent ovulation are:
- Birth control shot (DepoProvera)
- Hormonal Intrauterine Device (IUD)
- Progestin-only (mini) pill
- Contraceptive Implant (Nexplanon)
It is also important to note that failure to use the birth control methods correctly may result in failure to prevent ovulation and pregnancy.
How Can I Stop Ovulation Whilst on Birth Control?
You can consistently prevent ovulation whilst on birth control by taking the most effective birth control methods.
Combination birth control pills are one of the best, if not the best, options to reliably prevent ovulation and pregnancy- if taken correctly.
The NuvaRing and IUD are also great options, but must be replaced in order for it to work reliably.
To make the combination birth control pill even more reliable, it is a good idea to make taking the pill continuously a habit, as opposed to taking it for 21 days, followed by a 7-day break.
If you are taking the mini pill, using a backup birth control method, such as condoms, alongside the mini pill will make it much more reliable.
How to Stop Using Birth Control Pills

If you are taking hormonal birth control pills, and are ready to start trying to conceive (TTC), it is important that you know the side effects associated with stopping the pill.
Two to four weeks after stopping the pill, most women experience withdrawal bleeding. This period of withdrawal bleeding is considered your first period after stopping.
If you have been taking oral contraceptives, it may take one to three months before your menstrual cycle “levels out” again, and you have regular menstrual periods.
Once you stop taking the pill, and your estrogen levels begin to rise again, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Headaches
- Heavier Periods
- Fatigue
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Mood Swings
- Heightened sense of smell
Once the hormonal changes subside, and your hormone levels begin to regulate again, these side effects should subside.
It is important that you consult your doctor before changing your birth control method.
My name is Louise and I am the Digital Marketing and Administrative Assistant at MyBump2Baby. I have been writing in the parenting niche for over 2 years specialising in fertility, pregnancy, baby and baby name support articles.