Ovulation Symptoms & Signs
If you are trying to get pregnant, learning to recognise the common ovulation symptoms & signs can help you to time when you and your partner have sexual intercourse to increase your chances of conceiving.
In this article:
- What is Ovulation?
- Ovulation Symptoms and Signs
- When Do Women Ovulate?
- How Long Does Ovulation Last For?
- How Can I Predict Ovulation?
- When Should I Take an Ovulation Test?
- Ovulation FAQs
What is Ovulation?
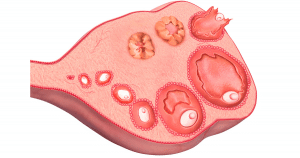
Ovulation is the process where an egg is released from one of your ovaries. The egg then travels down the fallopian tubes- where it can be fertilised by a sperm cell, resulting in pregnancy.
During the first half of your menstrual cycle, the egg matures within a follicle within the ovaries. This follicle then bursts and causes the egg to be released.
Ovulation typically happens once every menstrual cycle- although there are occasions where an egg may be released from both ovaries within 24 hours of one another. This is called hyper ovulation.
If you have a short menstrual cycle- it may also be possible to ovulate twice in a month– 3 weeks apart.
Ovulation usually occurs approximately 12-16 days before your next period is due to begin.
Ovulation Symptoms and Signs
During, or just before, ovulation you may experience the below ovulation signs:
Pelvic or Lower Abdominal Cramping
Mild pelvic or lower abdominal pain during ovulation is known as ovulation pain. It is also called “mittelscherz”- originating from the German words “middle” and “pain”.
Ovulation pain may feel like twinging or cramping in the middle of, or on one side of, your lower abdomen or pelvis. The pain may be located on the side from which the egg was released.
Ovulation pain may feel similar to your usual period cramps but occur around two weeks before your period is usually due.
It is commonly caused during the process of ovulation: when the egg enlarges, or when the follicle which is holding the maturing egg bursts.
Pelvic pain or abdominal pain during ovulation is experienced by approximately 40% of women who are 40 and under. For some women, this pain may be severe, and cause side effects such as nausea in cases of severe pain.
Light Spotting or Brown Discharge
Light bleeding or brown discharge is commonly caused by the rapid fluctuations in hormones that happen during ovulation- particularly the sudden decrease in estrogen levels that occur before ovulation. This sudden drop in your estrogen levels can cause the endometrium, or uterine lining, to shed.
Ovulation bleeding occurs during the middle of your cycle and is much lighter than your regular period- and much shorter in duration- lasting for only one to two days. Ovulation bleeding is pink or brown in colour.
If you experience spotting after ovulation, it may be a sign that you are pregnant. Spotting, due to pregnancy, is usually a sign that implantation has successfully occured– where a fertilised egg attaches to the lining of the uterus. The spotting caused by implantation is called implantation bleeding.
Changes in the Cervix
During ovulation, you may notice that your cervix feels different, or that it has changed position. This is completely normal.
During ovulation, your cervix typically moves higher up into the body, in order to transition into a position that is more ideal for sex, and for becoming pregnant.
When ovulation occurs, you become more fertile. When you are very fertile, the cervix becomes much softer and moister. This is because, during ovulation, cervical fluids are secreted to create the ideal environment for sperm to increase your chances of conception.
After ovulation has occurred, your cervix will drop down into a lower position and be easier to reach, and the cervix will return to its normal consistency.
Breast Tenderness
You may be wondering, do breasts hurt during ovulation?
It is commonly known that, just before, or during your period, your breasts feel heavy and ache. But can your breasts hurt during ovulation too?
You may have noticed that your breasts feel sore, achy or heavy around the middle of your cycle- when you ovulate.
Breast soreness or breast pain during ovulation is referred to as cyclical mastalgia.
Cyclical mastalgia is caused by the fluctuations of fertility hormones during ovulation, including follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estrogen, luteinizing hormone (LH), progesterone and Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
Breast pain relating to ovulation can begin as early as your LH surge, and finish once ovulation is over.
You can help to relieve cyclical mastalgia by avoiding caffeine, taking anti-inflammatory medication (such as ibuprofen or high-dose aspirin) and wearing a supportive, correctly-fitted bra.
Sore Nipples
As well as experiencing sore, achy breasts during ovulation, you may experience sore nipples. You may experience sore nipples at various points throughout your cycle, as well as ovulation.
During ovulation, you may experience pain in either one or both nipples. This is due to the rise in estrogen that occurs just before ovulation.
Diarrhea

Just before ovulation, your progesterone levels peak. This increase in progesterone can cause bowel issues.
The increase in progesterone can cause diarrhea during ovulation for some women and constipation in others, as well as bloating and abdominal cramping.
Bloating
Ovulation bloating usually occurs between the 11th and 14 day of your menstrual cycle- or just before, or on the day of, ovulation.
It may last for just a couple of hours, or up to two days.
Ovulation bloating may cause additional symptoms, such as abdominal pain on one side of their pelvis or lower abdomen.
Ovulation bloating is caused by the sudden changes in hormones that occur around the time of ovulation. In particular, the excess of estrogen may cause your body to retain more water, which can, in turn, cause bloating.
Heightened Sense of Smell
A heightened sense of smell is one of the potential ovulation symptoms and signs. If a smell that usually is delightfully intoxicating, suddenly seems far too strong or pungent and makes you curl your nose around the middle of your menstrual cycle- it may be a sign of ovulation.
Changes in Sex Drive
If you find that you are wanting sex much more during the middle of your cycle- or during ovulation- it is normal.
Just before and during ovulation, your estrogen and testerone levels are at their highest point- which causes a large increase in your libido.
This increase in libido coincides with your fertile window- and lasts for approximately 6 days- during the time in which you are able to conceive.
Your sex drive, or libido, will drop again once ovulation is over and your estrogen and testosterone levels decrease again.
In summary, changes in libido are one of the common ovulation symptoms and signs.
Nausea
We know that women experience nausea, or morning sickness, during pregnancy, but did you know that women can experience nausea during ovulation too?
Nausea during ovulation is caused by the sudden changes in estrogen levels and the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH). The sudden changes in these hormones can cause your stomach to produce more digestive fluids, which can in turn cause nausea.
During ovulation, some women may experience ovulation pain. Severe ovulation pain can cause nausea.
Factors that increase your chances of feeling nausea during ovulation are greasy and spicy foods, fertility treatments, large doses of vitamin C and anti-inflammatory medications.
You can help to relieve nausea during ovulation by reducing the amount of greasy and spicy foods you eat and by taking anti-nausea medications, being careful to read the side effects.
Headaches
It is common for women to experience migraines during or immediately after their menstrual period, or during ovulation.
These migraines are a form of hormonal migraine, and are called “menstrual migraines”.
You may also experience ovulation symptoms and signs such as fatigue, joint pain, acne, decreased urination or a lack of coordination with menstrual headaches and migraines.
Changes in Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus- or the fluid produced by your cervix- changes throughout your menstrual cycle. Cervical mucus changes can be an indication of ovulation.
Before ovulation occurs, your cervical mucus tends to be white, dry and thick. This cervical mucus is hostile to sperm.
However, just before ovulation occurs, your cervical mucus will become clear, thin, slippery and stretchy, with the consistency of egg whites. This egg white discharge creates the ideal environment for sperm to survive and reach the egg.
Some women chart their cervical mucus to try and predict their fertile window. This is called the cervical mucus method and is a form of natural family planning. Whilst the egg white discharge can be an indicator that you are ovulating, it is not a sure way to tell whether or not you are ovulating, as the egg-white cervical discharge (EWCM) often occurs before ovulation, and before your fertile window begins.
Experiencing egg white or creamy discharge after ovulation may be a sign of pregnancy.
Weight Gain
Weight gain is one of the often unwanted, yet common, ovulation symptoms. Weight gain during ovulation is caused by the increase in estrogen, which is paired up with a decrease in progesterone. Throughout ovulation, these hormonal changes can cause an increase in appetite.
In addition to this, having low progesterone and high estrogen over a longer period of time may result in weight gain. Other causes of weight gain during ovulation include:
- Menopause
- Changes in insulin levels
- Life style or diet changes
- Water retention
- Changes in appetite
When Do Women Ovulate?
Knowing when and how long you ovulate for is important if you are trying to get pregnant.
The typical menstrual cycle lasts anywhere between 21 and 35 days, and some women have regular, consistent menstrual cycles, whereas, other women may have menstrual cycles that are inconsistent in length: or irregular cycles.
Experts state that ovulation usually occurs around 14 days before a woman’s period is due, but if you have an irregular menstrual cycle, it may result in irregular ovulation.
Causes of irregular menstrual cycles include:
- Birth control
- Ovulation disorders (such as polycystic ovary syndrome or hypothalamic dysfunction)
- High stress levels (high stress levels are known to influence fertility of the female reproductive system)
- Obesity
- Low body weight
- Extreme exercise
Women ovulate when they experience a surge in luteinizing hormone. When the LH surge occurs, the mature egg leaves the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilised.
How Long Does Ovulation Last For?
Ovulation occurs once every menstrual cycle and typically lasts for half a day (12 hours) to a day (24 hours).
A woman’s fertile window, however, lasts for up to 6 days.
If you are wondering how long an ovulation test stays positive, you can find out here How Long will an Ovulation Test Stay Positive?
What is Your Fertile Window?
If you are fertile, it means that you are able to reproduce or have children.
The fertile window is the days during the menstrual cycle in which you are able to become pregnant- also known as the pregnancy window.
The few days in which you are able to conceive is called your fertile window. If you are trying to conceive, the fertile window is the best time for intercourse.
Your fertile window includes the days leading up to ovulation, and the day of ovulation itself.
A woman’s fertile window is typically 6 days long- and includes the rate of sperm survival, as well as the day of ovulation.
Ovulation lasts only for one day, but sperm can live for up to 5 days before an egg cell is released, which means you may be able to become pregnant, even if you have sex 5 days before you are due to ovulate! This means the fertile window lasts for a total of 6 days.
How Can I Predict Ovulation?
Predicting when you ovulate, and when your fertile window will most likely be, drastically improves your chances of conception. You can predict when you will next ovulate by tracking ovulation with a variety of methods:
Menstrual Charting
Menstrual charting is the method of charting your menstrual cycle to figure out how long it lasts. For most women, their menstrual cycle lasts for 28 days- where day one is the day that your period begins.
Since women’s cycles often vary in length from month to month, you should chart your menstrual cycle for several months to find the average length.
Monitoring Basal Body Temperature
Basal body temperature (or BBT) is an individual’s at-rest temperature. To track when ovulation is, women can chart their basal body temperature.
For women with regular cycles, ovulation happens approximately 14 days before their periods. Before ovulation, your temperature decreases slightly- to around between 36.4 degrees celcius and 36.4 degrees celcius.
Between 12 and 24 hours after the egg is released, your temperature rises to between 36.4 degrees celcius and 37 degrees celcius and stays at the risen temperature for several days. Your basal body temperature can also drop as part of your normal menstrual cycle. Do you know when? Read our article “When Does BBT Drop If Not Pregnant?” to find out.
You are able to track your menstrual cycle, and when ovulation will occur, by measuring your basal body temperature every morning. You should measure your basal body temperature at the same time every morning and record your results on a chart.
If your cycle is regular, you can use the charted BBT results to tell when you will ovulate next.
Ovulation Kits
Ovulation predictor kits can be used to predict when you are ovulating and are particularly useful for women who have irregular menstrual cycles, and therefore can’t use the menstrual charting method.
Ovulation test kits test your urine for the luteinising hormones released during, or just before, ovulation. This is called an LH surge.
If you would like an ovulation predictor kit, they can be found at a store or in your local pharmacy.
If you have been using ovulation tests, you be may wondering can an ovulation test detect pregnancy? You can read our article to find out.
Ovulation Calculators
An ovulation calculator or ovulation calendar can aid you in finding out when your peak fertile days will be.
Ovulation calculators are used to estimate your potential ovulation days. Ovulation calculators do this by taking the date of your last period and your average cycle length.
Ovulation calculators often generate ovulation calendars in order to chart your potential fertile days.
Fertility Monitors
A fertility monitor is a device that is used to track your basal body temperature and fertility hormone levels in your saliva, urine or cercal fluid.
The use of a fertility monitor can help you to learn more about your menstrual cycle and predict when your fertile window, and when ovulation, will be.
There are three different kinds of fertility monitors: digital monitors, thermometers and wearable fertility monitor devices.
When Should I Take an Ovulation Test?
If you have a regular menstrual cycle, you should start taking ovulation tests 4-5 days before your predicted ovulation date. However, if you usually have irregular menstrual cycles, which fluctuate in length from month-to-month, you should begin testing daily from each day after your period ends.
The best time of day to take an ovulation test is between 10am and 12pm- or with the second morning urine.
The reason you should take an ovulation test with your second-morning urine, as opposed to your first, is because, if your luteinising hormone surge occurs first thing in the morning, the increase in luteinizing hormone will likely not show until approximately 4 hours later- or when you have your second urination.
Taking an ovulation test at your first urination of the day can result in a negative ovulation test.
Ovulation FAQs
Does Plan B Work During Ovulation? – The answer to this question is no; the morning after pill does not work during ovulation. The morning after pill is designed to delay ovulation, in order to prevent pregnancy. If you are ovulating already, the morning after pill will have no effect.
How long after an LH surge do you ovulate? – You begin ovulation approximately between 24 and 36 hours after a luteinizing hormone surge.
Can you ovulate without a period? – It is possible to ovulate and not have a period afterwards, just as it is possible to have periods but not experience ovulation each month in a cycle called an “anovulatory cycle”.
When to have sex after an LH surge? – The best time to have sex after an LH surge varies from woman-to-woman. You can find out more by reading our article.
Do Breasts Hurt During Ovulation? Some women may experience breast pain during ovulation. You can find out the causes and symptoms by reading our article.
What are the Signs Ovulation is Over? There are signs that may show that ovulation is over- with a key one being the change in your vaginal discharge. Read the article to find out more!
Why not check out our next article? You can read it here Plan B Spotting VS Implantation Bleeding.
More from MyBump2Baby
To read about pregnancy symptoms at each day past ovulation, click the links below:
- 1DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 2 DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 3 DPO Symptoms
- 4 DPO – Early Pregnancy Symptoms
- 5 DPO – Early Pregnancy Symptoms
- 6DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 7 DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 8 DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 9 DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 10 DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 11DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 12 dpo – Early Pregnancy Symptoms
- 13 DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
- 14 DPO Pregnancy Symptoms
My name is Louise and I am the Digital Marketing and Administrative Assistant at MyBump2Baby. I have been writing in the parenting niche for over 2 years specialising in fertility, pregnancy, baby and baby name support articles.